Asset Turnover Ratio Formula + Calculator
September 14, 2023

On the other hand, in industries with few competitors or high barriers to entry, companies might not face the same pressure, which could result in lower asset turnover figures. Conversely, a declining enrolled agents vs cpas trend might raise red flags about potential operational stagnation or the obsolescence of assets. A company will gain the most insight when the ratio is compared over time to see trends.
Asset Turnover in Return on Assets
After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers. Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts.
Is it better to have a high or low total asset turnover?
From the asset turnover ratio calculation done, Walmart, Target, AT & T, and Verizon had an asset turnover ratio of 2.29, 1.99, 0.31, and 0.42 respectively. Recall that the asset turnover ratio is most useful when compared across similar companies. Therefore, it would not make sense to compare the asset turnover ratios for Walmart or Target with that of AT&T or Verizon, because they operate in very different industries. As the asset turnover ratio varies across business sectors, some industries tend to have a higher ratio while some tend to have a lower ratio.
What is the fixed asset turnover?
The ratio calculates the company’s net sales as a percentage of its average total assets to show how many sales are generated from each dollar of the company’s assets. For instance, an asset turnover ratio interpretation of 1.5 would mean that each dollar of the company’s assets generates $1.5 in sales. The fixed asset turnover ratio formula divides a company’s net sales by the value of its average fixed assets. Publicly-facing industries including retail and restaurants rely heavily on converting assets to inventory, then converting inventory to sales.
Asset Turnover Ratio: Understanding Its Significance and Limitations in Financial Analysis
As different industries have different mechanics and dynamics, they all have a different good fixed asset turnover ratio. For example, a cyclical company can have a low fixed asset turnover during its quiet season but a high one in its peak season. Hence, the best way to assess this metric is to compare it to the industry mean. After understanding the fixed asset turnover ratio formula, we need to know how to interpret the results.
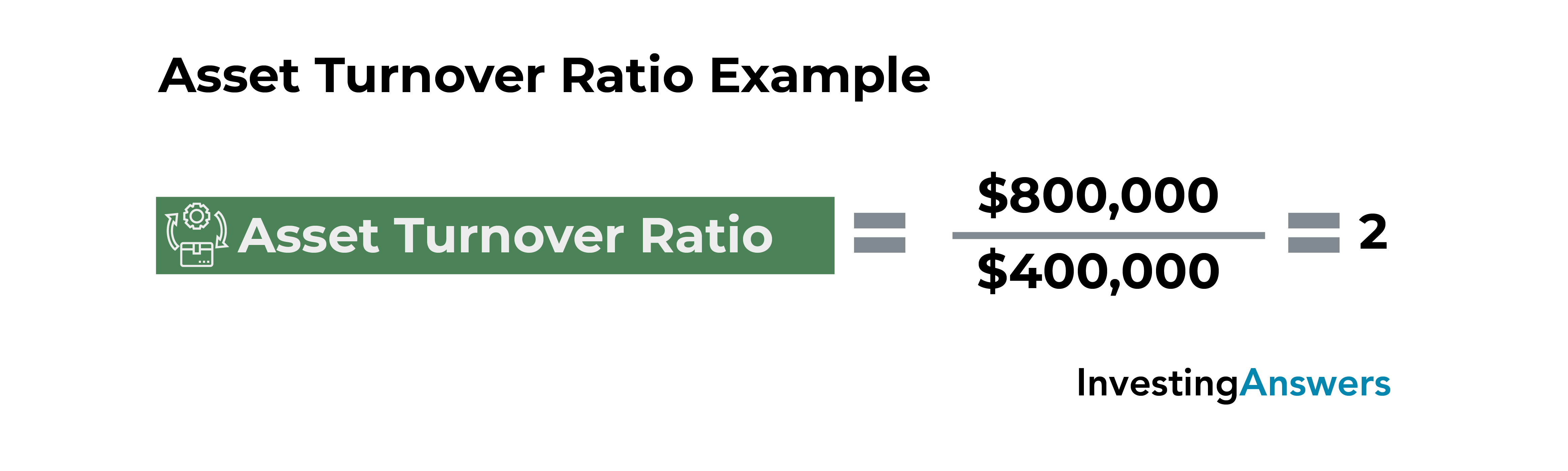
Hence, it would not be proper to compare this ratio for businesses in different sectors. You can locate your net sales number on your income statement (also known as your profit and loss statement). This is your total sales number, minus any returns, damaged goods, missing goods, etc. Rather than gross sales, your net sales is the more accurate figure to use when you’re generating your asset turnover ratio. Remember that net sales only accounts for the products that end up in your customers’ hands at the end of the year—in other words, what they actually paid for. The asset turnover ratio formula is net sales divided by average total sales.
These fields rely heavily on infastructure and machinery, which can slow down asset turnover. If the asset turnover ratio of a company is less than 1, it is said to have a low ratio. This is not considered good for the company because it indicates that the company’s total assets cannot produce enough revenue at the end of the accounting period (usually a year). However, this interpretation and conclusion still depend on the average asset turnover ratio of the industry to which the company belongs. Other business sectors like real estate normally take long periods of time to convert inventory into revenue.
However, interpreting this value as being good will also depend on the average asset turnover ratio of the industry to which the company belongs. It is generally preferable for the interpretation of asset turnover ratio to be a higher value. A high asset turnover ratio indicates that the company is more efficient in generating revenue from its assets. If the asset turnover ratio of a company is greater than 1, it is considered a high ratio. Although there’s no single key to a successful business, it’s often the business owners who’ve figured out how to run a lean business that enjoy long, prosperous futures.
- The fixed asset focuses on analyzing the effectiveness of a company in utilizing its fixed asset or PP&E, which is a non-current asset.
- The ratio calculates the company’s net sales as a percentage of its average total assets to show how many sales are generated from each dollar of the company’s assets.
- Therefore, it would not make sense to compare the asset turnover ratios for Walmart or Target with that of AT&T or Verizon, because they operate in very different industries.
- By using this ratio, companies can evaluate their productivity in using assets that are on hand.
- The asset turnover ratio is most helpful when compared to that of industry peers and tracking how the ratio has trended over time.
Publicly-facing industries such as retail and restaurants tend to have a higher asset turnover ratio. This explains why the asset turnover ratio of Walmart and Target is way higher than Verizon and AT &T for the same year. As we can see from the calculation done, Verizon and AT&T both had an asset turnover ratio of less than one.
That’s because this ratio gives creditors a direct line of sight into whether or not your company is optimally managed. This figure represents the average value of both your long- and short-term assets over the past two years. To reach this number, you’ll need (unsurprisingly) two years of asset totals; you can find this information on your accounting balance sheet.
