What is depreciation expense?
January 6, 2022

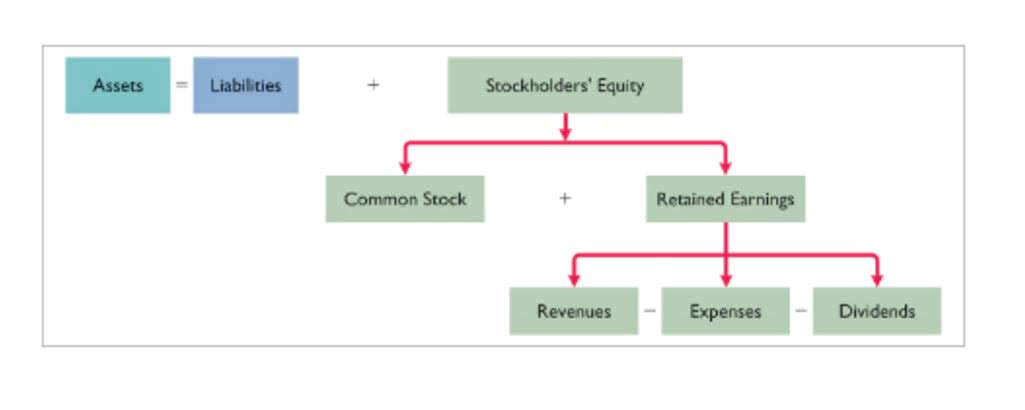
The main drawback of SYD is that it is markedly more complex to calculate than the other methods. The depreciation expense reduces the carrying value of a fixed asset (PP&E) recorded on a company’s balance sheet based on its useful life and salvage value assumption. The method records a higher expense amount when production is high to match the equipment’s higher usage. Depreciation recapture is a provision of the tax law that requires businesses or individuals that make a profit in selling an asset that they have previously depreciated to report it as income. In effect, the amount of money they claimed in depreciation is subtracted from the cost basis they use to determine their gain in the transaction.
Sec. 163(j) business interest limitation: New rules for 2022 – The Tax Adviser
Sec. 163(j) business interest limitation: New rules for 2022.
Posted: Thu, 01 Dec 2022 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Those include features that add value to the property and are expected to last longer than a year. For the sake of this example, the number of hours used each year under the units of production is randomized. To help you get a sense of the depreciation rates for each method, and how they compare, let’s use the bouncy castle and create a 10-year depreciation schedule. This formula is best for production-focused businesses with asset output that fluctuates due to demand. This formula is best for companies with assets that lose greater value in the early years and that want larger depreciation deductions sooner.
Sum-of-the-Years’ Digits Depreciation
So, even though you wrote off $2,000 in the first year, by the second year, you’re only writing off $1,600. In the final year of depreciating the bouncy castle, you’ll write off just $268. To get a better sense of how this type of depreciation works, you can play around with this double-declining calculator.
- Then, we can extend this formula and methodology for the remainder of the forecast.
- The declining balance method is a type of accelerated depreciation used to write off depreciation costs earlier in an asset’s life and to minimize tax exposure.
- When you depreciate assets, you can plan how much money is written off each year, giving you more control over your finances.
- The double-declining balance (DDB) method is an even more accelerated depreciation method.
- Depreciation is a way for businesses and individuals to account for the fact that some assets lose value over time.
Depreciated cost is the value of a fixed asset minus all of the accumulated depreciation that has been recorded against it. In a broader economic sense, the depreciated cost is the aggregate amount of capital that is “used up” in a given period, such as a fiscal year. The depreciated cost can be examined for trends in a company’s capital spending and how aggressive their accounting methods are, seen through how accurately they calculate depreciation. Depreciation allows businesses to spread the cost of physical assets over a period of time, which can have advantages from both an accounting and tax perspective.
Depreciated Cost: Definition, Calculation Formula, Example
Instead of realizing the entire cost of an asset in year one, companies can use depreciation to spread out the cost and match depreciation expenses to related revenues in the same reporting period. This allows the company to write off an asset’s value over a period of time, notably its useful life. SYD suits depreciation expense meaning businesses that want to recover more value upfront, but with more even distribution than they would otherwise get using the double-declining method. The SYD method’s main advantage is that the accelerated depreciation reduces taxable income and taxes owed during the early years of the asset’s life.